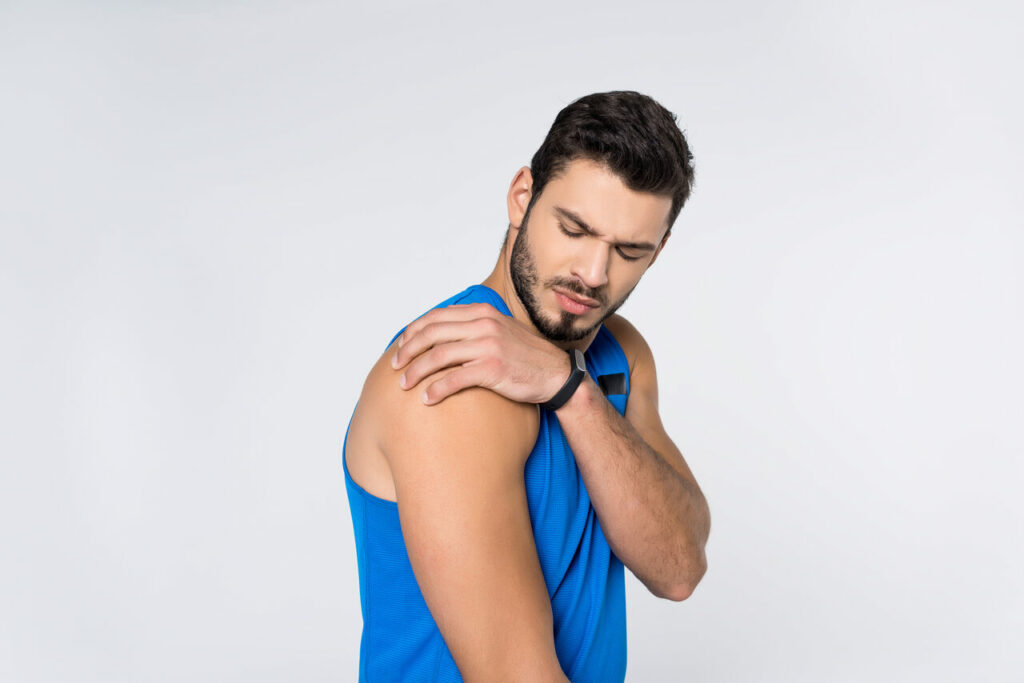
Have you ever wondered about that nagging shoulder pain during your morning jog or while lifting groceries? It might be more than just a simple strain. Rotator cuff tears, a common yet often overlooked issue, can be the culprit behind your shoulder discomfort.
This guide dives into the essential aspects of rotator cuff tears, from their anatomy to effective management strategies, to illuminate this important health topic.
What is a Rotator Cuff Tear?
A rotator cuff tear is a partial or complete injury of one or more tendons that comprise the rotator cuff. The rotator cuff is a group of four muscles and their accompanying tendons that surround and stabilize the shoulder joint.
This structure allows for smooth and pain-free movement, but when it gets damaged, it can result in severe pain and weakness in the affected shoulder.
These injuries are not just a sports issue, though. They can affect a wide range of people. Here are vital groups commonly affected by this condition:
- People over 40: Age-related wear and tear is a primary factor.
- Athletes: Especially those in sports requiring repetitive shoulder movements like tennis, swimming, or baseball pitching.
- Occupational Hazards: Workers in jobs demanding overhead reaching or heavy lifting, such as carpenters, construction workers, and painters.
- Individuals with a history of shoulder injuries: Previous injuries can predispose one to rotator cuff problems.
- Those with certain medical conditions: Some systemic diseases or conditions can increase vulnerability to rotator cuff injuries.
It’s important to understand that while these groups are more commonly affected, anyone can experience a rotator cuff injury.
Anatomy of the Shoulder: The Rotator Cuff Explained
We’ve briefly touched on who gets affected by rotator cuff injuries, but let’s delve into the anatomy involved.
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles essential for shoulder movement and stability. It includes four muscles:
- Subscapularis
- Infraspinatus
- Teres Minor
- Supraspinatus
Remember these with the mnemonic “SITS.”
The shoulder’s glenohumeral joint, a ball and socket structure, is highly mobile and unstable.
Stability is maintained by static stabilizers (like the joint capsule and ligaments) and dynamic stabilizers, which include the rotator cuff muscles and the long head of the biceps brachii. This complex system allows for a wide range of shoulder movements.
Causes of Rotator Cuff Tears
So, what makes the rotator cuff prone to injuries? There are several ways a tear can occur, including:
- Repetitive Stress: Repeated shoulder use in sports or jobs can lead to wear and tear.
- Acute Injury: Sudden, forceful movements, like lifting something too heavy, can cause tears.
- Age-Related Degeneration: As we age, our muscles and tendons naturally weaken, increasing the risk of tears.
- Poor Blood Supply: Reduced blood flow to the rotator cuff with age can hinder repair and maintenance, leading to tears.
Aside from these causes, genetics, anatomical variations, and certain diseases or conditions also make someone more susceptible to rotator cuff injuries.
Common Activities Leading to Tears
Certain activities commonly lead to rotator cuff tears, such as:
- Sports: Sports involving overhead movements, like baseball, tennis, and swimming, put a lot of stress on the rotator cuff.
- Manual Labor Jobs: Construction or plumbing jobs require repetitive shoulder use with heavy lifting, which can cause tears.
- Falls: Falling onto an outstretched arm can cause a powerful force on the rotator cuff, leading to tears.
Combined with the abovementioned causes, these activities can weaken and damage the rotator cuff over time, making it more prone to tears.
Recognizing Symptoms of a Rotator Cuff Tear
You might mistake a rotator cuff tear for a simple shoulder strain, but there are some critical differences in symptoms to watch out for. Some common symptoms of a rotator cuff tear include:
- Pain at Rest and Night: This pain is often felt when lying on the affected shoulder. It can be a constant aching that disrupts sleep and rest, indicating inflammation or aggravation in the rotator cuff.
- Weakness: This manifests as difficulty performing activities that require lifting the arm, like reaching overhead or behind. It’s a sign that the rotator cuff muscles are not functioning correctly.
- Cracking Sensation: Also known as crepitus, this sensation occurs when moving the shoulder in specific ways. It’s often due to tendons rubbing against each other or other structures in the shoulder.
- Limited Range of Motion: A noticeable decrease in the ability to move the shoulder can indicate a tear. This limitation can make daily activities like combing hair or reaching for items challenging.
- Swelling and Tenderness: These are common inflammatory responses and may be felt around the shoulder joint, indicating tissue trauma or irritation.
- Pain when Lifting or Lowering Arm: This pain occurs during specific movements and can range from a dull ache to a sharp pain, signalling that specific actions exacerbate the tear.
You can consult with a physiotherapist or chiropractor to get a proper diagnosis and treatment plan for your potential rotator cuff tear. If left untreated, a rotator cuff tear can worsen over time and may even require surgery to repair the damaged tissue.
Treatment Options for Rotator Cuff Tears
Treatment for rotator cuff tears varies based on the severity of the tear and the individual’s lifestyle. Options range from conservative methods to surgical intervention. Non-surgical treatments include:
- Rest
- Ice
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Physical therapy
These approaches focus on reducing pain and inflammation and strengthening shoulder muscles. Surgery may be necessary to repair the torn tendon in more severe cases. Treatment choice depends on factors like the patient’s age, activity level, and the tear’s specifics.
What to Expect from Surgery
Surgery for a rotator cuff tear is rare, surgery aims to reattach the torn tendon to the bone.
Common surgical methods include arthroscopic tendon repair, open tendon repair, and tendon transfer. Arthroscopic surgery is minimally invasive, using small incisions and a camera.
Open surgery is more extensive and may require large or complex tears. Recovery time and rehabilitation depend on the surgery type, with a general focus on restoring full shoulder function.
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy
Post-surgery or as part of non-surgical treatment, rehabilitation and physical therapy is crucial. A physiotherapist will guide you through exercises to improve flexibility, strength, and range of motion. Initially, therapy might focus on gentle movements to reduce stiffness, gradually progressing to strengthening exercises.
The rehab program is tailored to individual needs to return to normal activities safely and effectively. Regular sessions and adherence to prescribed exercises are critical for successful recovery.
Prevention and Maintaining Shoulder Health
Preventing rotator cuff tears involves a mix of awareness, exercise, and lifestyle adjustments. It’s essential to recognize that while not all tears can be prevented, reducing risk is possible with the right approach.
- Regular Exercise: Strengthening and stretching shoulder muscles helps maintain joint stability and flexibility.
- Proper Technique: Using correct form during sports and activities can minimize stress on the shoulder.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: For those with jobs involving repetitive shoulder use, ergonomic changes can reduce strain.
Incorporating these preventive measures into your routine can significantly decrease the likelihood of experiencing a rotator cuff tear. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional, especially if you’re in a high-risk group, can also be beneficial.
Empower Your Shoulder Health Journey with Aspire Physiotherapy
Are you ready to take control of your shoulder health? Look no further than Aspire Physiotherapy. With two locations in Edmonton, Ellerslie and Century Park.
Our team of experienced physiotherapists specializes in treating and preventing rotator cuff tears, using evidence-based techniques to help you achieve optimal results. Our individualized rehab and physical therapy approach ensures you receive the best care possible for your unique needs.Schedule a consultation with us today and let our experts guide you towards a pain-free, healthy shoulder.